Using the Virtual Endpoint middleware with Tyk OAS APIs
Last updated: 5 minutes read.
The virtual endpoint middleware provides a serverless compute function that allows for the execution of custom logic directly within the gateway itself, without the need to proxy the request to an upstream service. This functionality is particularly useful for a variety of use cases, including request transformation, aggregation of responses from multiple services, or implementing custom authentication mechanisms.
The middleware is configured in the Tyk OAS API Definition. You can do this via the Tyk Dashboard API or in the API Designer.
If you’re using the legacy Tyk Classic APIs, then check out the Tyk Classic page.
Configuring the middleware in the Tyk OAS API Definition
The design of the Tyk OAS API Definition takes advantage of the operationId defined in the OpenAPI Document that declares both the path and method for which the middleware should be added. Endpoint paths entries (and the associated operationId) can contain wildcards in the form of any string bracketed by curly braces, for example /status/{code}. These wildcards are so they are human readable and do not translate to variable names. Under the hood, a wildcard translates to the “match everything” regex of: (.*).
The virtual endpoint middleware (virtualEndpoint) can be added to the operations section of the Tyk OAS Extension (x-tyk-api-gateway) in your Tyk OAS API Definition for the appropriate operationId (as configured in the paths section of your OpenAPI Document).
The virtualEndpoint object has the following configuration:
enabled: enable the middleware for the endpointfunctionName: the name of the JavaScript function that will be executed when the virtual endpoint is triggeredbody: [optional] abase64encoded string containing the JavaScript codepath: [optional] the relative path to the source file containing the JavaScript codeproxyOnError: [optional, defaults tofalse] a boolean that determines the behaviour of the gateway if an error occurs during the execution of the virtual endpoint’s function; if set totruethe request will be proxied to upstream if the function errors, if set tofalsethe request will not be proxied and Tyk will return an error responserequireSession: [optional defaults tofalse] a boolean that indicates whether the virtual endpoint should have access to the session object; iftruethen the key session data will be provided to the function as thesessionvariable
Note
One of either path or body must be provided, depending on whether you are providing the JavaScript code in a file or inline within the API definition. If both are provided then body will take precedence.
For example:
|
|
In this example the virtual endpoint middleware has been configured for requests to the GET /anything endpoint. We have also configured the following custom attributes in the pluginConfig section of the API definition:
{
"map": {
"key": 3
},
"num": 4,
"string": "example"
}
The body field value is a base64 encoded string containing this JavaScript code, which will be invoked by the virtual endpoint middleware:

function myVirtualHandler (request, session, config) {
var responseObject = {
Body: "Virtual Endpoint "+config.config_data.string,
Headers: {
"foo-header": "bar",
"map-header": JSON.stringify(config.config_data.map),
"string-header": config.config_data.string,
"num-header": JSON.stringify(config.config_data.num)
},
Code: 200
}
return TykJsResponse(responseObject, session.meta_data)
}
A call to the GET /anything endpoint returns:

HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Fri, 01 Mar 2024 12:14:36 GMT
Foo-Header: bar
Map-Header: {"key":3}
Num-Header: 4
Server: tyk
String-Header: example
Content-Length: 24
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
Virtual Endpoint example
The configuration above is a complete and valid Tyk OAS API Definition that you can import into Tyk to try out the virtual endpoint middleware.
Configuring the middleware in the API Designer
Adding a Virtual Endpoint to your API endpoints is easy when using the API Designer in the Tyk Dashboard, simply follow these steps:
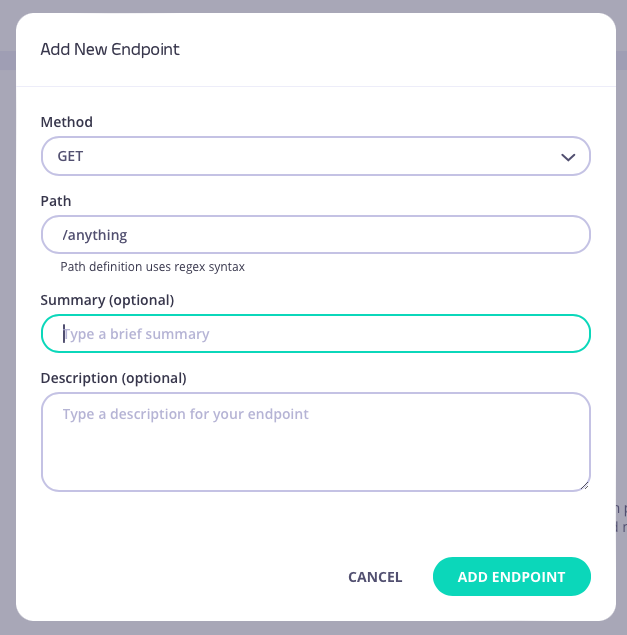
Step 1: Add an endpoint
From the API Designer add an endpoint that matches the path and method to which you want to apply the middleware.
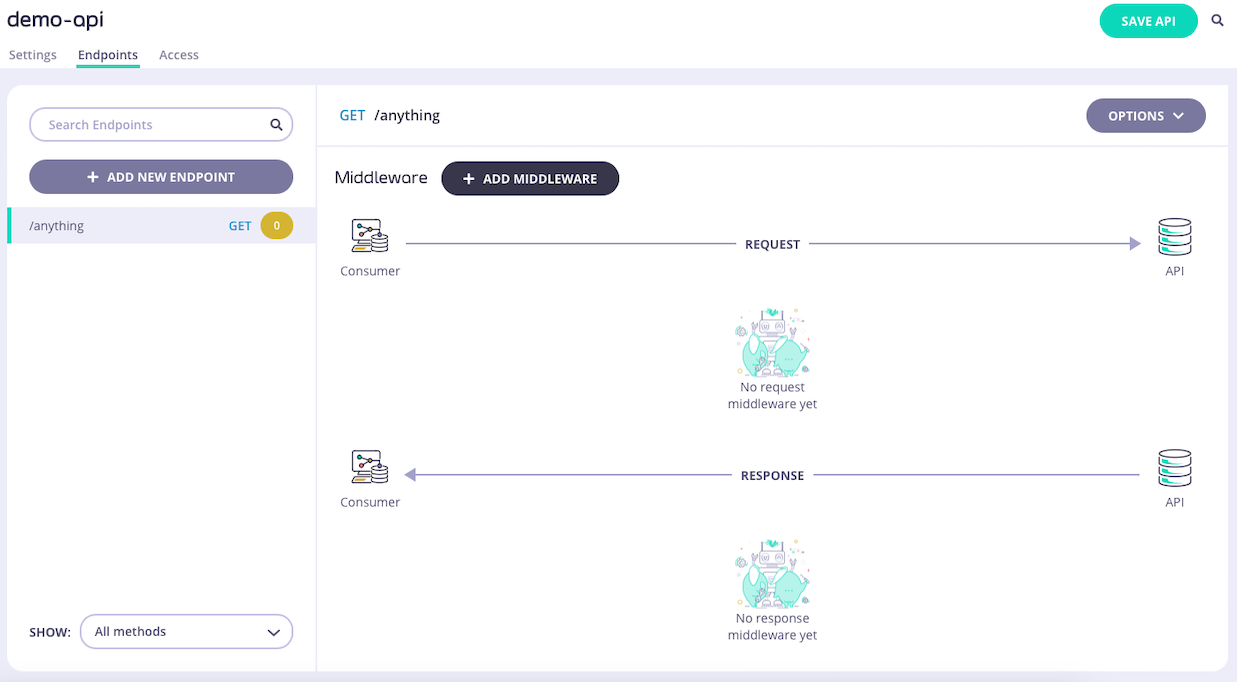
Step 2: Select the Virtual Endpoint middleware
Select ADD MIDDLEWARE and choose Virtual Endpoint from the Add Middleware screen.
Step 3: Configure the middleware
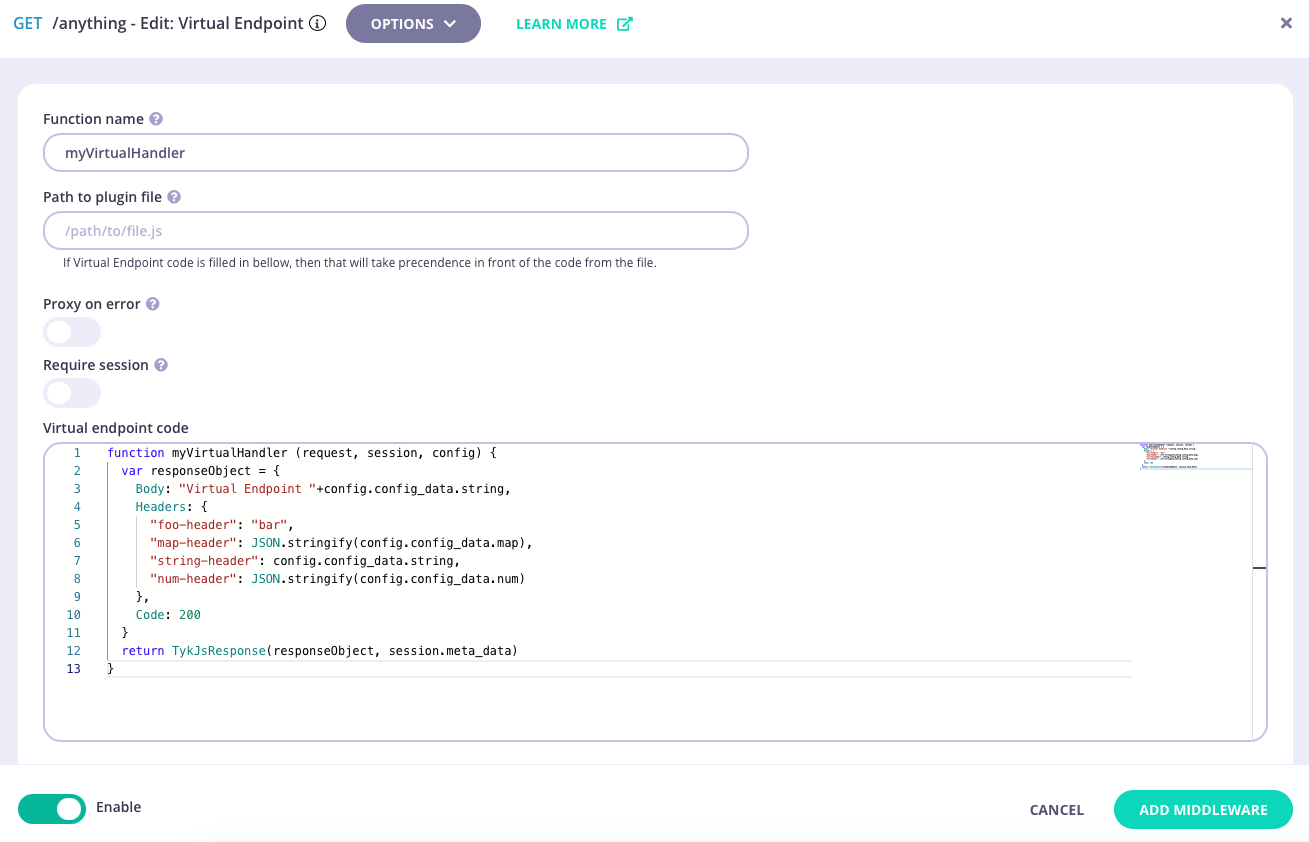
Now you can provide either the path to a file containing the JavaScript function to be run by the middleare, or you can directly enter the JavaScript in the code editor.
For both sources, you must provide the function name that should be called when the middleware executes.
You can also optionally configure the behaviour required if the function should return an error and also indicate to Tyk whether the virtual middleware requires access to the key session metadata.
Step 4: Save the API
Select ADD MIDDLEWARE to save the middleware configuration. Remember to select SAVE API to apply the changes.