Upgrading On Debian - DEB
Last updated: 5 minutes read.
The following guide explains how to upgrade Tyk Self-Managed running on Debian
Upgrade Guide Video
Please refer to our upgrade guide video below for visual guidance of upgrading Tyk Self-Managed (DEB).
Preparations
After reviewing guidelines for preparing for upgrade, follow the instructions below to upgrade your Tyk components and plugins.
Upgrade order: Please note that upgrade order is as explained in the upgrade overview
Distro versions
Tyk supports the following version for Debian and its derivative Ubuntu:
| Distribution | Version |
|---|---|
| Debian | 11 |
| Ubuntu | 20 |
| Ubuntu | 18 |
| Ubuntu | 16 |
Our repositories will be updated at https://packagecloud.io/tyk when new versions are released.
During the initial deployment of Tyk, your team may have utilized APT repositories or directly downloaded the .deb files. To verify the presence of APT repositories on the server, inspect the following locations:
- Dashboard:
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/tyk_tyk-dashboard.list - Gateway:
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/tyk_tyk-gateway.list - Pump:
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/tyk_tyk-pump.list
If the above files are not present, it could be worth checking internally that the initial deployment was done by manually downloading and installing the .deb files. This is common in airtight environments without internet access.
Verify Target Package Availability
Depending on the Linux distribution that you are using, ensure that you are pulling the correct version and distribution from the packagecloud.io/tyk repository.
The package name contains the version number and the distro/version column displays the specific distribution release.
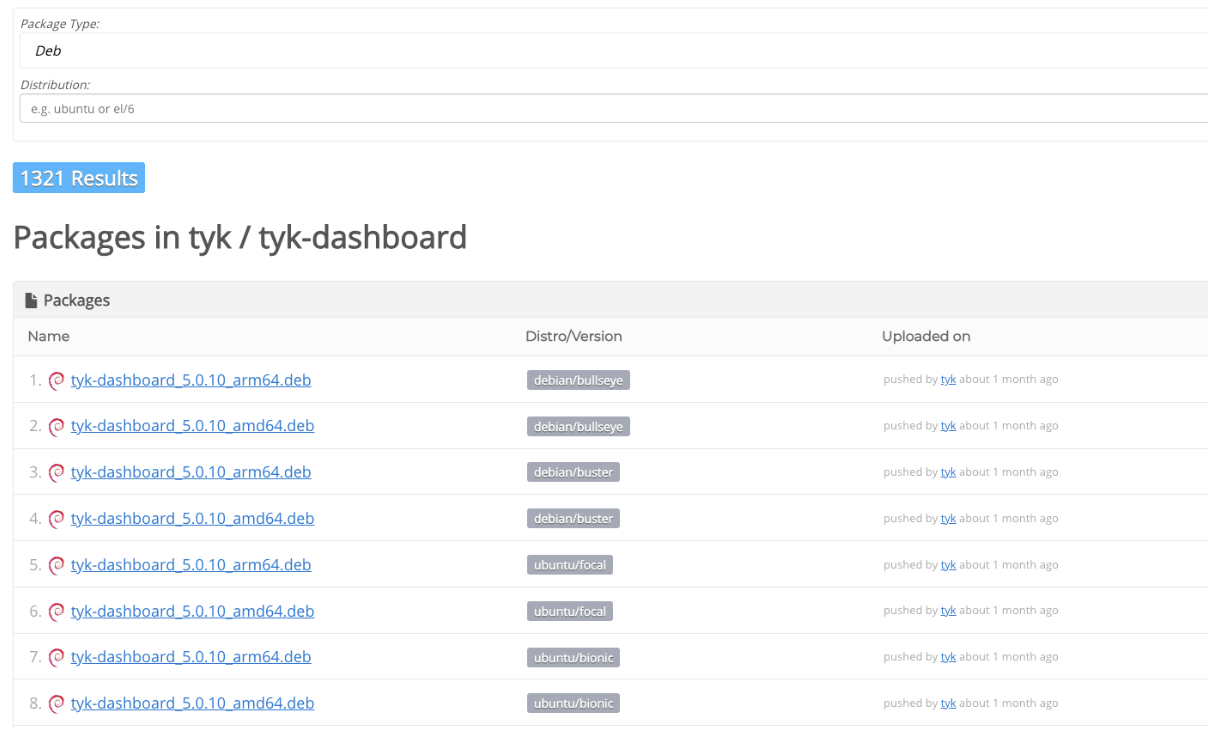
Backups
Configuration files:
Please take a backup of below configuration files of each Tyk component. This will be useful in case you need to cross reference configuration changes or need to rollback your deployment.
- Dashboard Configuration File:
/opt/tyk-dashboard/tyk_analytics.conf - Gateway Configuration File:
/opt/tyk-gateway/tyk.conf - Pump Configuration File:
/opt/tyk-pump/pump.conf
Databases
Redis
For more detailed instructions on managing Redis backups, please refer to the official Redis documentation: https://redis.io/docs/management/persistence/
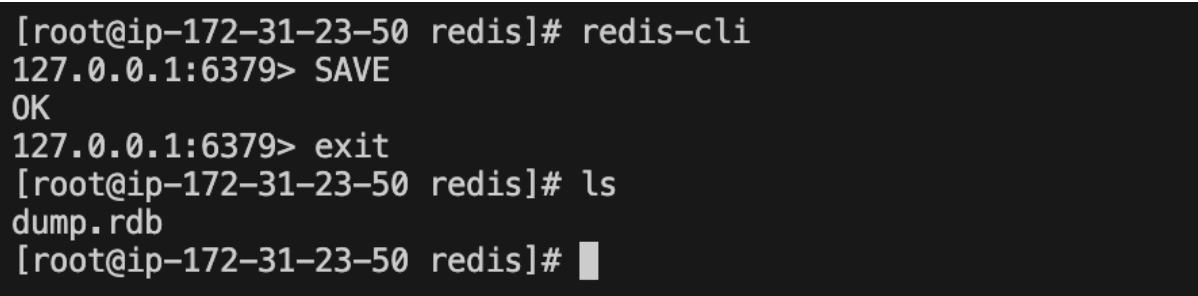
The Redis SAVE command is used to create a backup of the current redis database. The SAVE command performs a synchronous save of the dataset producing a point in time snapshot of all the data inside the Redis instance, in the form of an RDB file.
# Using SAVE, if the previous dump.rdb file exists in the working directory, it will be overwritten with the new snapshot
SAVE
Example - SAVE
To restore Redis data, follow these steps:
- Move the Redis backup file (dump.rdb) to your Redis directory.
- Start the Redis server
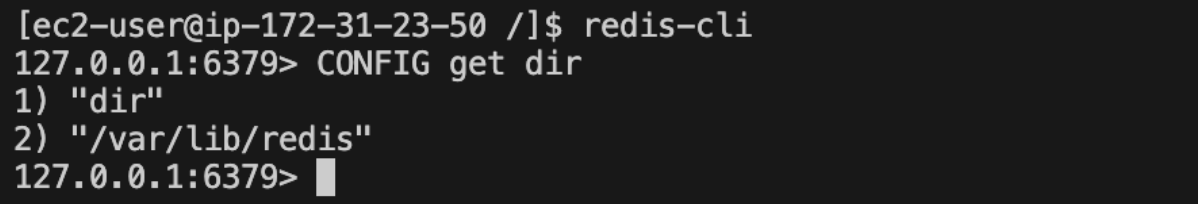
To locate your Redis directory, you can use the CONFIG command. Specifically, the CONFIG GET command allows you to read the configuration parameters of a running Redis server.
Example - CONFIG
MongoDB
For detailed instructions on performing backups in MongoDB, please refer to the official MongoDB documentation: https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/backups/
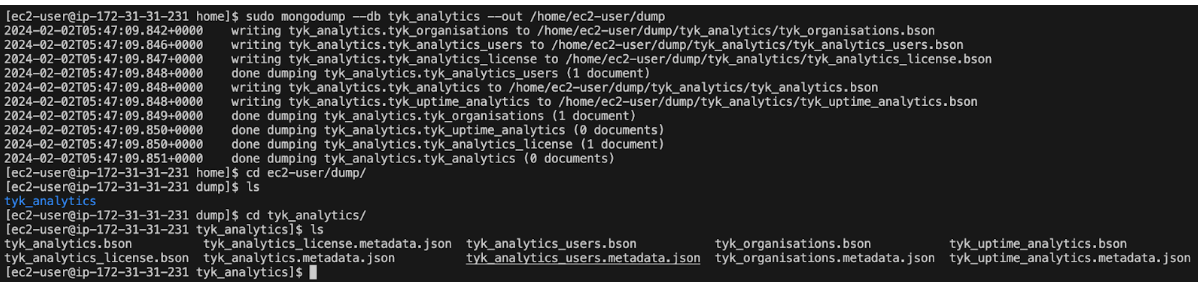
To capture a snapshot of a MongoDB database from a remote machine and store it locally, utilise the mongodump command on the primary node. Specify the host and port number (default is 27017) of the remote server, along with additional parameters such as the database name, user credentials and password. Lastly, designate the directory where the snapshot should be created.
mongodump --db tyk_analytics --out /path/to/dump/directory
Example
To restore a database using a previously saved snapshot, simply employ the mongorestore command.
mongorestore --host <hostname> --port <port> --username <username> --password <password> /path/to/dump/directory
Upgrade Tyk Packages
Before executing the upgrade, ensure that you have consulted and performed all the necessary steps in the pre upgrade checklist.
1. Update Tyk Repositories
Fetch and update information about the available packages from the specified repositories.
sudo apt-get update
2. Verify availability of target upgrade packages
List current versions of Tyk using the command below:
dpkg -l | grep -i tyk
Example

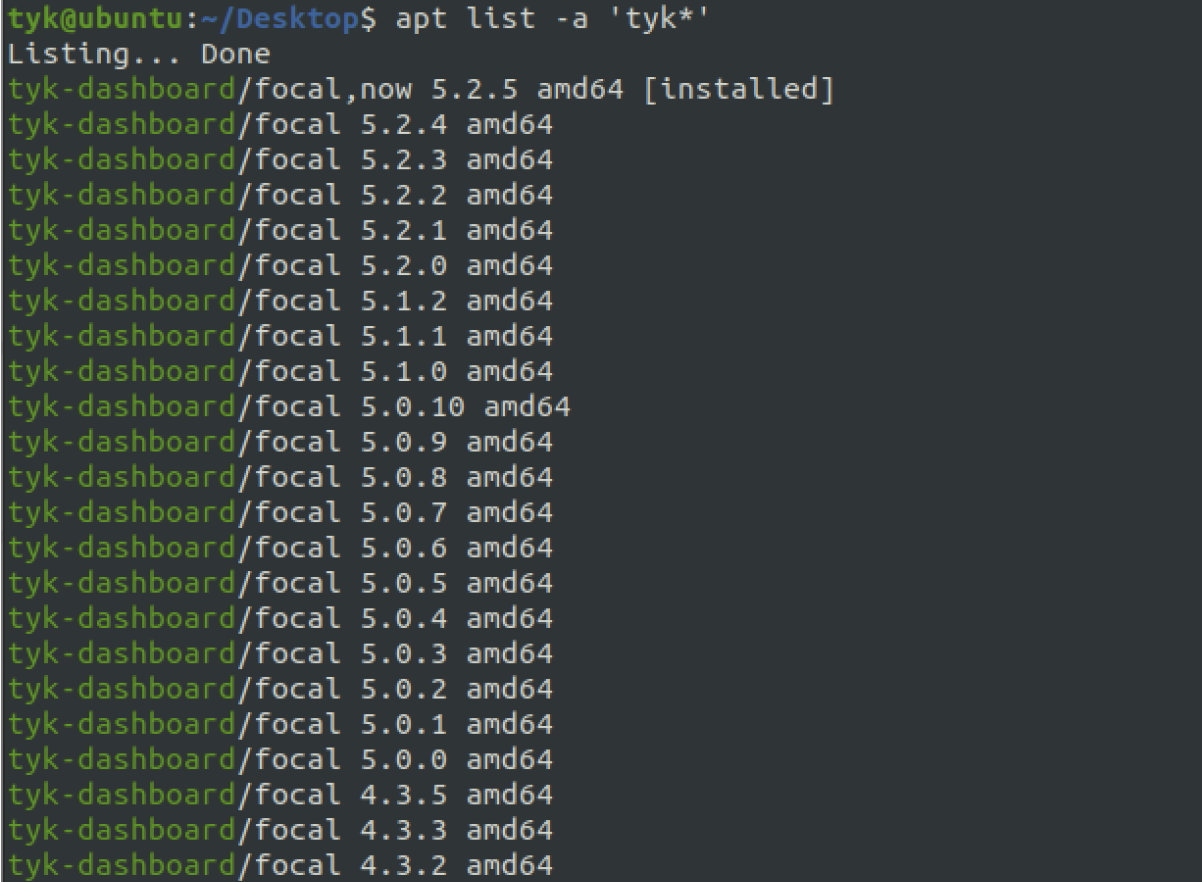
List available versions of upgradable packages of Tyk components and ensure that the version you are planning to upgrade to is listed in the output of the above command.
apt list -a 'tyk*'
Example
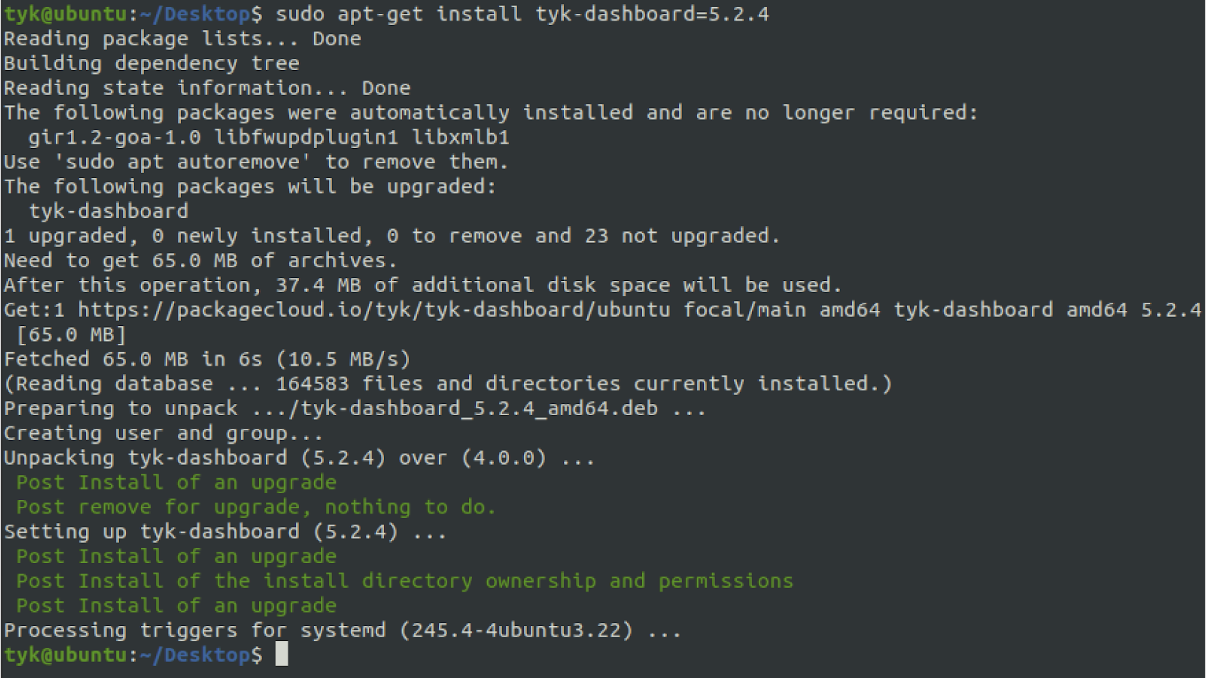
3. Upgrade Tyk Components
Note: Please specify the exact version you are upgrading into.
sudo apt-get install tyk-dashboard=<desired-version>
sudo apt-get install tyk-gateway=<desired-version>
sudo apt-get install tyk-pump=<desired-version>
Example
4. Restart Components
After upgrading Tyk, restart the services
# Restart Services
systemctl restart tyk-dashboard
systemctl restart tyk-gateway
systemctl restart tyk-pump
# Check status of Tyk Components
systemctl status tyk-dashboard
systemctl status tyk-gateway
systemctl status tyk-pump
5. Health check on upgraded Tyk components
Perform a health check on all 3 Tyk Components. The host and port number varies on your setup.
Tyk Dashboard
curl http://localhost:3000/hello
Tyk Gateway
curl http://localhost:8080/hello
Tyk Pump
curl http://localhost:8083/health
Revert the upgrade
If the upgrade fails you can revert to the old version by following the steps below.
1. Inspect package logs
In case the upgrade fails for some reason, you can use the command below to check your history of package installs:
cat /var/log/apt/history.log
2. Revert
Manually reverting to a previous version can be done by installing or uninstalling a package. For instance, to roll back to the previous version, you can use this command:
sudo apt-get install tyk-dashboard=<previous version>
These commands are provided as general guidelines and should be used with caution. It’s advisable to consult with your system administrator or seek assistance from a qualified professional before executing any system-level commands